By Mohammad Monirul Hasan, Foresight4Food FoSTr Bangladesh Facilitator
In December 2024, I had the privilege to participate in the Delivering for Nutrition (D4N) in South Asia: Connecting the Dots Across Systems conference, held in Colombo, Sri Lanka. This significant event, hosted by IFPRI in collaboration with CGIAR and regional partners, convened experts and stakeholders to tackle South Asia’s enduring nutrition challenges. Given the region’s double burden of malnutrition—persistent undernutrition alongside a surge in obesity and non-communicable diseases—the discussions underscored the urgent need for integrated, forward-thinking strategies to ensure sustainable nutrition security. Here are some of my insights from the conference.
Harnessing Foresight Research for Food Systems Transformation

At the conference, I had the privilege of presenting our research on foresight-driven food systems transformation and the Diet Scenario 2050 for Bangladesh, a project supported by Oxford University, Wageningen University & Research, and GAIN. Our research employs foresight methodologies to anticipate future food system trajectories and design actionable pathways toward nutrition security. By leveraging scenario-building and participatory modeling, we explore how household decision-making, agricultural innovations, and policy interventions can collectively enhance food system resilience.
The Crucial Role of Foresight in Addressing Nutrition Challenges
The conference highlighted foresight methodologies as crucial tools for anticipating emerging trends and informing adaptive policy responses. In dialogues with IFPRI’s Foresight Team and CGIAR’s Food Systems Hub representatives, we explored critical gaps in food systems research and discussed collaborative approaches to align foresight insights with policy and investment strategies. Our discussions identified opportunities for:
- Evidence-Based Policymaking: Using foresight outputs to inform national and regional policy frameworks.
- Scenario Analysis: Modeling climate impacts, dietary shifts, and technological advancements to guide policy development.
- Cross-Sector Collaboration: Engaging agriculture, health, and education sectors to build integrated solutions.
Regional Collaboration and Investment for Food Systems Transformation
The conference provided a unique platform for fostering regional partnerships. Through interactions with policymakers, development agencies, and investors, we identified actionable steps to promote cross-border foresight initiatives that can enhance food systems resilience across South Asia. Key takeaways included:
- Shared Learning Platforms: Promoting knowledge exchange across countries to address common nutrition challenges.
- Regional Investment Frameworks: Encouraging collaborative investments in sustainable food systems and nutrition programs.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Mobilizing resources from diverse sectors to scale impactful innovations.



Insights for Policy and Practice: Moving Forward with Foresight
Key lessons from the conference emphasized the transformative power of foresight for achieving sustainable nutrition outcomes:
- Anticipatory Governance: Foresight can help policymakers proactively address emerging risks and opportunities.
- Systems Thinking: Integrating health, agriculture, and socio-economic perspectives is crucial for holistic solutions.
- Multi-Sectoral Collaboration: Effective partnerships between governments, academia, and the private sector are essential for impactful interventions.
- Investment Alignment: Foresight insights can guide investors to support high-impact initiatives that promote nutrition security.
Conclusion: Shaping the Future of Food Systems in South Asia
This conference reinforced the value of foresight methodologies in driving evidence-based decisions and fostering regional cooperation. It provided a platform to showcase Bangladesh’s commitment to forward-looking strategies and collaborative approaches that address the interlinked challenges of nutrition, climate resilience, and food security. Building on these insights, I look forward to advancing partnerships and implementing foresight-driven initiatives that contribute to sustainable food systems transformation across South Asia.
By Bram Peters
The future of food systems is uncertain, yet one thing is clear—transformative change is urgently needed. Climate change, inequality, and geopolitical instability are reshaping how food is produced, distributed, and consumed. How can we navigate these complexities and create a more sustainable, resilient food system?
At the Power of Foresight Workshop held on 30-31 January 2025 at the FAO headquarters in Rome, experts and practitioners gathered to discuss how foresight can drive food systems transformation. Their insights reveal a crucial truth: the process itself— working with complexity, embracing inclusivity, diverse perspectives, and collective intelligence—is central to making real progress.
Insights from the ‘Power of Foresight’ Workshop
- 17 different cases and the stories of 48 participants from 27 countries demonstrated that foresight approaches have much to offer to the process of food systems transformation
- Working with complex systems is what it’s about, and effective foresight practices for food systems change to embrace this
- Openness to new and inclusive perspectives should be central to all foresight for food systems transformation efforts
- The process brings the answer – and foresight can bring awareness of crucial process elements such as collective intelligence, agency, time and scale
- Embracing the ‘ifs’: how you do foresight, and what comes before and after, is just as important as the development of scenarios
- Foresight is not one approach or one methodology – there are a diversity of ways to go about it
- The national food systems pathways can benefit from foresight approaches



Photos: 30 January 2025, Foresight4Food workshop. FAO Headquarters, Rome. Photo credit: ©️FAO/Cristiano Minichiello
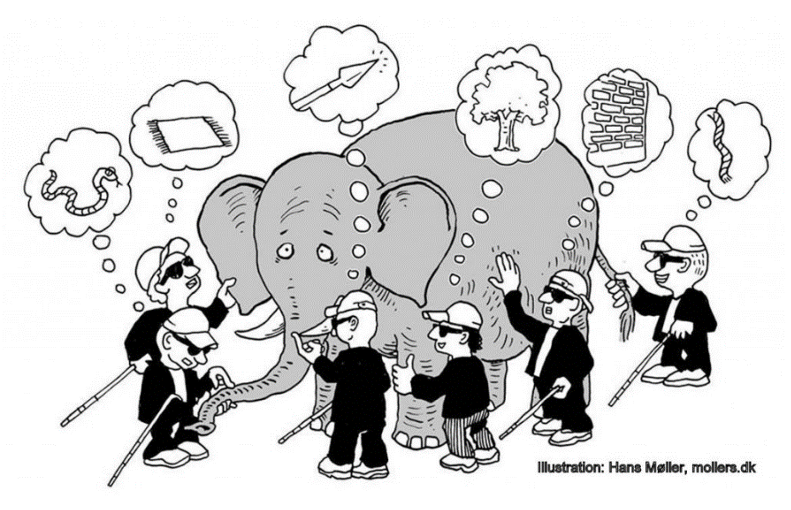
Working with complex systems: Let’s talk about the elephants in the room
When it comes to food systems transformation, there isn’t just one elephant in the room—there are many. These metaphorical elephants represent the complex, interconnected challenges we face, and ignoring them only hinders progress.
- First, as a whole range of interrelated challenges and assumptions we are not working on enough: whether that’s climate change, human rights, global geopolitical turbulence, growing inequality. All these challenges together form a context of global polycrisis.
- Second, we can see elephants in the room related to our apparent inability to take decisive transformative action in food systems: a lot of talk, limited action.
- Finally, we can see elephants as representing systems. An elephant can represent a dynamic, complex food system, of which we might only be able to see or understand the trunk, tusks, ears or tail.
Like the elephant and the blind men metaphor (see image to the right), food systems are deeply interconnected with global issues like climate change, inequality, and geopolitical instability. Tackling these requires a holistic approach, recognizing that transformation cannot happen in silos.
Gather new and inclusive perspectives – and change your own
What’s central to talking about complex food systems is perspective. We all have different mental images of food systems—whether local agriculture, marine ecosystems, or trade networks. Expanding our perspectives helps identify new entry points for addressing issues like malnutrition, poverty, and sustainability.

For some, like from the Pacific region, it’s about marine ecosystems in which food is central. Changing your perspective can be a helpful way of looking at a complex topic: such as to see the Pacific food system composed not of ‘small island states’ but rather ‘large ocean states’ connected with the global food system through trade, governance, and oceanic currents. Why is flipping your perspective so important? It helps to reframe entry points for discussion with other stakeholders and view the root causes of things like malnutrition, non-communicable diseases, poverty and human rights abuse in food systems differently.
If you are able to change your perspective, it helps to understand the viewpoints of those less heard. Having an inclusive process to gather different viewpoints is crucial to changing perspectives and behaviour, mobilising for collective action and creating shared visions of the future.
The process is the answer
Ever tried herding cats? Well, transforming food systems is about fostering C.A.T.S.—a process centred on:
- Collective intelligence – Multi-stakeholder collaboration and co-creation
- Agency – Empowering change through action
- Time – Bridging past, present, and future
- Scale – Recognizing interconnections between local and global systems
So, what does it mean to herd cats when talking about food systems? It means there are no magic bullets: the process is central to the outcome.
Effort on addressing the ‘ifs’
Foresight can be of great added value to support the food systems transformation process. Whether it is about co-creating alternative futures, conducting backcasting towards a more desirable scenario, highlighting the cost of delayed action, or informing anticipatory policy – foresight and scenario tools are a key toolbox in the hands of systems change champions.
In order for foresight to be effective, there are a number of conditional ‘ifs’ i.e., if foresight experts and facilitators:
- Are able to move beyond added value, tackling pre-conditions, obstacles, and constraints affecting how stakeholders prepare for the future.
- Not only preach to the converted – we need to involve stakeholders who think and act differently
- Are cognizant of power differences, lock-ins and political economy
- Build on other approaches that also provide value, such as design thinking, human-centred development and mission-oriented policy making.
- Pay attention to what comes before and after the development of scenarios
Scenarios only developed from the perspective of single organisations or without meaningful consultation and dialogue will not be effective.
Foresight approaches and national food systems pathways
There are a broad range of foresight approaches, some expert-driven or participatory, others quantitative, experiential, creative or analytical. Each has their value – but these needs come from a clear user need and scope within a food system. However, it is essential to keep in mind that foresight is a tool, not a panacea, and cannot address all questions.
With 156 national convenors driving progress through implementing 137 national food systems transformation pathways, the upcoming UNFSS+4 Stocktaking Moment (July, Addis Ababa) presents an opportunity to share lessons and strengthen impact. What we have seen the past two days in Rome, is the incredible richness and diversity of initiatives that use foresight to support the food systems transformation process.
Sharing the lessons from these initiatives, communicating the potential of foresight, and supporting the national convenors to further realise the impact on transforming food systems outcomes will be crucial in the run-up to the Stocktaking Moment.
By Herman Brouwer, WUR lead for FoSTr and Wangeci Gitata-Kiriga, FoSTr Country Facilitator Kenya
How can foresight transform the lives of pastoralists, fishers, and farmers in Marsabit County, Kenya? Marsabit County faces formidable challenges, with the escalating impacts of climate change threatening its food systems and livelihoods. Despite decades of significant support from development partners and government initiatives, the tangible results remain limited. This begs the critical question, inspired by David Peter Stroh: Why, despite our collective best efforts, have we struggled to foster lasting, positive change in Marsabit’s food systems?
Foresight could hold the key. By enabling stakeholders to anticipate future challenges, identify sustainable solutions, and adapt to evolving realities, foresight offers a transformative approach to addressing the county’s persistent issues. It’s time to rethink strategies and align efforts to create meaningful, long-term change for Marsabit’s pastoralists, fisherfolk, and farmers.
We brought stakeholders together in December 2024 to explore the above question, and to make a start to imagine different futures for the food system in Marsabit. Naturally, this involved a highly interactive discussion on the current food system and how we got to this situation – using a data walk with up-to-date data and analysis, as well as system maps. This provided the basis to jointly understand the dynamics of how food systems change (or resist change) and imagine how the food system could change even further in the next 10-15 years. The stories that participants came up with, based on their lived experiences in four distinct sub-counties of Marsabit, evolved into four scenarios. We used one of these scenarios (the ‘ideal one’ called Ajako, meaning ‘paradise’ in the Borana language) to create a vision for the future. We then identified the initial pathways and building blocks required to work towards this Ajako scenario.



Photo credit: Crispaus Onkoba/SID, used with permission
That’s the summary of where we ended up. However, an essential detail was omitted earlier: How do you ensure the right individuals and institutions are in the room? Achieving this required a carefully planned stakeholder engagement process, which began several weeks before the workshop. The process involved numerous meetings with individual stakeholders across the county to understand who was doing what, who was most invested, what had been successful, and what hadn’t worked in the past. The ultimate goal was to mobilize the most relevant and diverse stakeholders for the 3-day workshop.
We started by engaging the county leadership, relevant government departments, and development partners. But stakeholder mobilization didn’t stop there. We actively sought out voices often overlooked in food systems discussions: faith-based organizations, community groups, and private sector representatives.
Following the workshop, we ensured the initial excitement and momentum were sustained by maintaining contact with key participants. This effort culminated in the formation of a County Development Group, coordinated by the county government. This group brings together all actors actively engaged in food security initiatives, creating a collaborative platform for sustained impact.
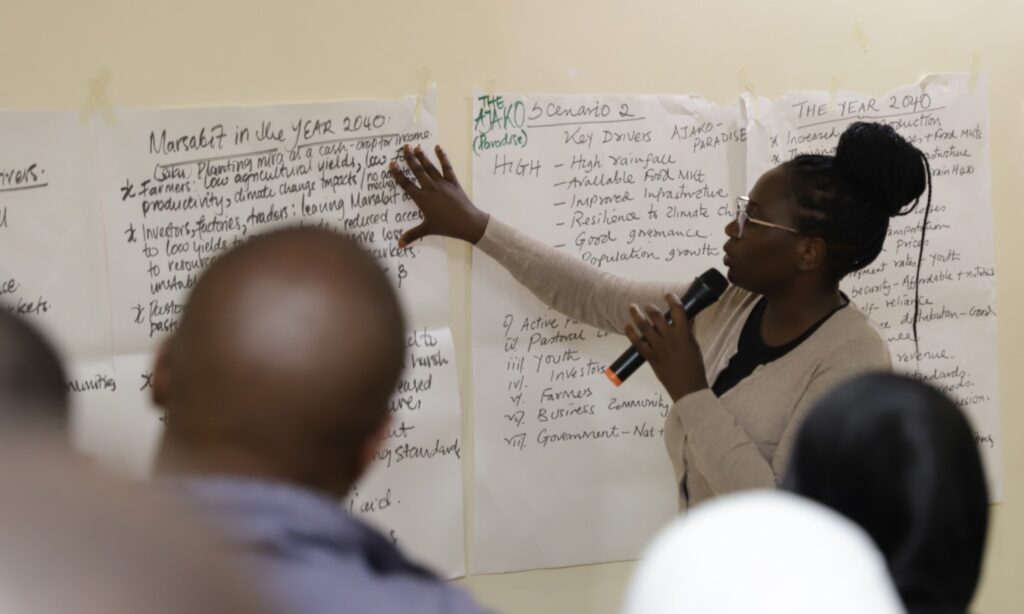



Photo credit: Crispaus Onkoba/SID, used with permission
We argue that the investment in stakeholder engagement has been the most valuable ingredient of the foresight process so far. It has allowed our Kenya foresight team to obtain the right endorsements and buy-in at the right levels. Without getting the engagement process right, all participatory foresight tools, and supportive analytics, are at risk of falling flat.
There is a case to be made to only report on foresight processes after they are concluded, rather than at the start. This blog is an exception, to make the point that how you start matters.
The FoSTr Kenya foresight team, consisting of Results for Africa Initiative (RAI); Society for International Development (SID); International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI); University of Nairobi; Food and Land Use Coalition (FOLU); Wageningen University & Research (WUR); and the University of Oxford, will continue to support the County Development Group in Marsabit to coordinate actions of state and non-state actors towards achieving Ajako by 2040. A similar process is taking place in Nakuru County. Both have active linkages to Kenya’s national food system science-policy interfaces.
By Jim Woodhill – Lead Foresight4Food Initiative
It was great to participate in the next phase of Jordan’s journey toward food systems transformation as part of the Foresight4Food Initiative. This significant step brought together around fifty key stakeholders on November 11 to discuss strategies for accelerating change.
The discussions built on earlier work from the Foresight4Food FoSTr Programme in Jordan, including scenario analyses developed during previous workshops, computer modelling results, and a series of policy briefs. These resources provided a foundation for the day’s explorations into actionable pathways for transforming Jordan’s food systems.
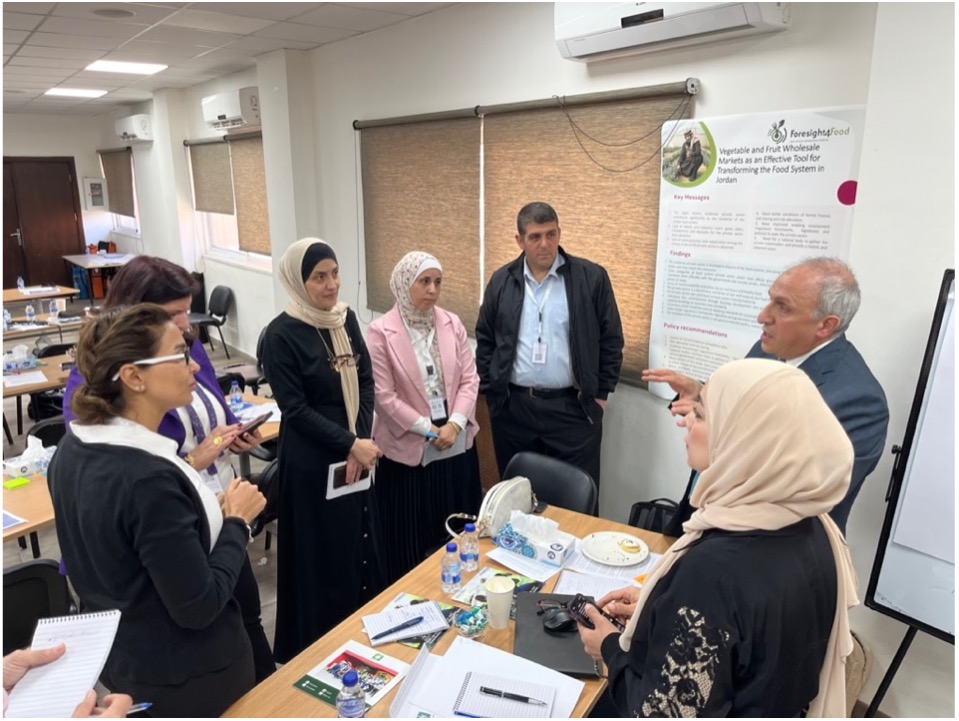

A key highlight of the workshop was the collaborative spirit among diverse stakeholders. This environment fostered consensus-building around critical challenges and opportunities. Participants examined deep-seated barriers to change, focusing on economic and social incentives, the power dynamics of various actors, and entrenched mindsets that hinder progress.
Drawing from detailed policy briefs on topics such as vegetable and fruit markets, food governance, the role of the private sector, and the contributions of civil society, the workshop delved into strategies for enabling meaningful change.
Informed by the policy papers on vegetable and fruit markets, food governance, the role of the private sector and the role of civil society, the workshop looked more deeply into how change can be brought about.
One particularly impactful aspect was the use of computer modelling, conducted with Wageningen University and Research’s MAGNET model. This analysis demonstrated the potential consequences of continuing current practices (“business-as-usual”) versus adopting healthier, more sustainable pathways. Such data-driven insights are instrumental for policymakers, equipping them with evidence to support investments and policy reforms.
Beyond the workshop, conversations with Jordanian universities explored integrating foresight and systems thinking into academic curricula. Additionally, a dedicated training session provided researchers and policymakers with hands-on experience using the MAGNET model to analyze food system changes.
The workshops were made possible with support from the Jordanian Hashemite Fund for Human Development (JOHUD) and the National Alliance Against Hunger and Malnutrition (NAJMAH), underscoring the importance of partnerships in driving food systems transformation.
By Zoe Barois
Like many other countries, Bangladesh is working to develop it’s Food Systems Transformation Action Plan. This will be presented during the United Nations Food Systems Summit Plus 4 Stocktaking event. On November 6 and 7, Foresight4Food collaborated with GAIN Bangladesh to host a workshop on how foresight could contribute to the development of the Action Plan.
If transforming food systems were easy, it would have been done! But it’s not. Discussions dug into deeper questions about HOW change can be brought about and the implications of this for action in Bangladesh.
The participatory and dynamic workshop brought together policymakers, researchers, youth leaders, key UN organisations and members of the private sector. The workshop served two purposes, first to help clarify directions for the Action Plan, and secondly, to take forward the work on using foresight to help drive food systems change.
Discussion during the workshop focused on the five commitment pathways:
- Nourish all people
- Boost Nature-based Solutions
- Advance Equitable Livelihoods, Decent Work & Empowered Communities
- Build Resilience to Vulnerabilities, Shocks and Stresses and
- Accelerating the Means of Implementation
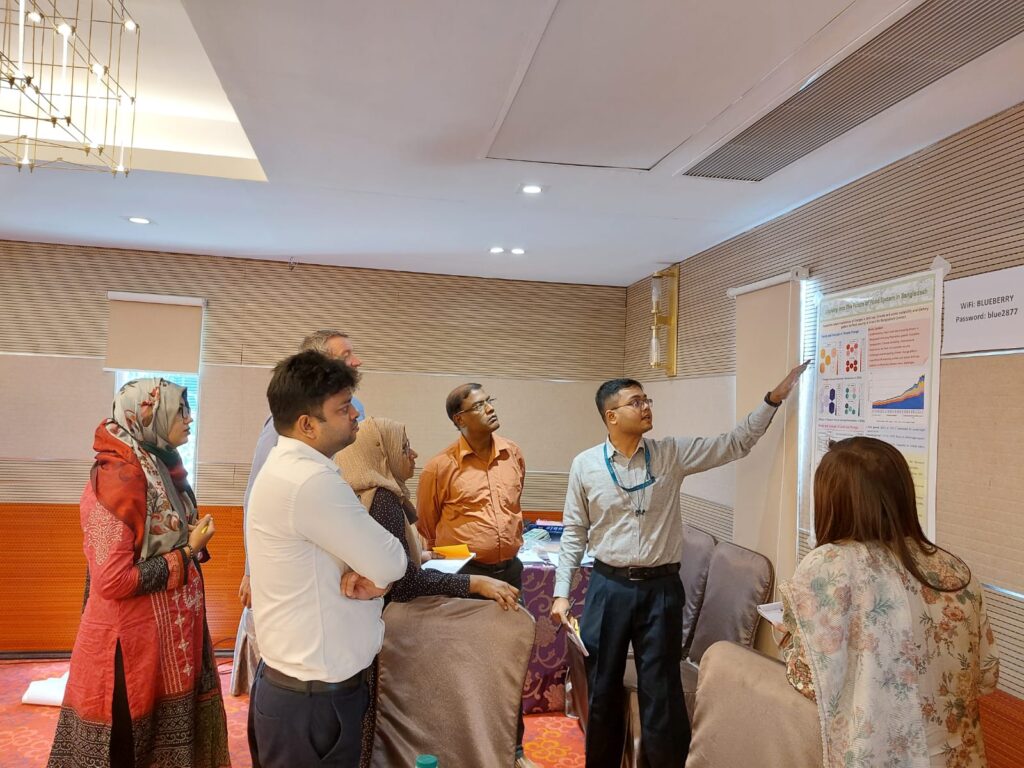
Validating scenarios for the future of food systems in Bangladesh
It was great to engage in discussions around four visual future scenarios. These were developed using rich pictures during a lively multistakeholder event in June earlier this year. Future scenarios are an excellent way to open discussions around what different stakeholders see as a desirable future. Interestingly, these do not always align as the implications would vary depending on what outcomes you’re seeking. At the end of the day, a poor farmer will desire different things when compared to a corrupt businessman!
The scenarios displayed different outcomes based on these uncertainties:

Equity – Would there be high or low levels of equity?
Climate resilience – we all know that climate change is happening, but whether Bangladesh will have high or low climate resilience is definitely in question
Healthy food consumption – Would people in Bangladesh be eating traditional diets or would they follow a diet that resembles something like a North American diet, something seen in many parts of the world.
Business structure – would Bangladesh have a diversified or consolidated business structure, dominated by a few large conglomerates
Creatively naming these scenarios helps convey the messages. So we had a fun exchange where groups came up with poetic Bangladeshi names to better describe the scenarios. Part of the validation will be to update these, helping spur action towards the most desired and away from the least desired future.
Unpacking five critical issues
Key issues blocking progress towards food systems change in Bangladesh relate to:
- The cost of a healthy diet in addressing malnutrition
- Climate resilience
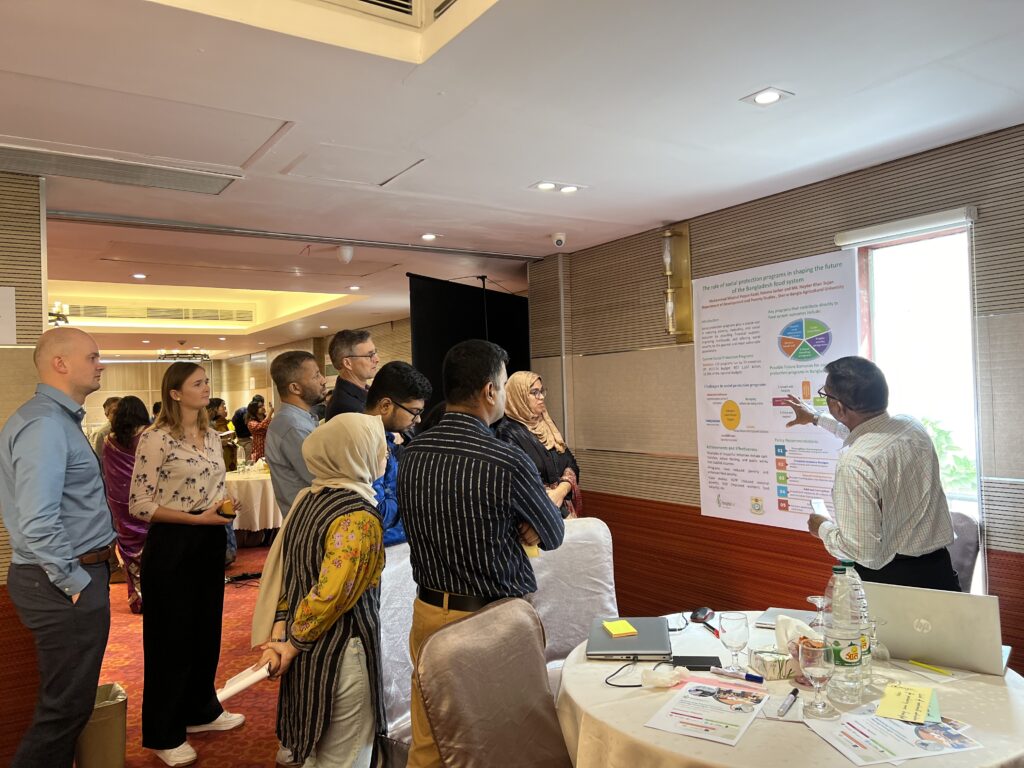
- The role of social protection programmes in shaping food systems change
- Fruit and vegetable production
- Land use change and dietary patterns
These key themes were the result of a longer participatory process that emerged from the food systems map of Bangladesh. Diving into these topics, FoSTr’s five research partners shared their work on the key trends, challenges, and opportunities within each theme. Exploring these themes using a future lens can help clarify desired directions of change.
The power of causal loop mapping
How often do you get policymakers, youth and researchers around one table, heavily immersed in discussion using sticky notes and flip charts? My response: not often enough! This combination of actors is rarely seen but proves oh so valuable in uncovering insights previously hidden from each sector. The tool casual loop mapping, may be familiar to some. It’s a systems thinking tool where the interconnections between elements are mapped and the direction of causality identified. It’s a great way to map out the elements within a system and identify levers of change – small actions that lead to a large impact. For each of the commitment pathways, this casual loop mapping was performed. Insights like forming alliances between farmers and entrepreneurs to boost sustainable farming practices, or using the power of advertising to improve healthy food consumption and inspire healthy lifestyles were uncovered.
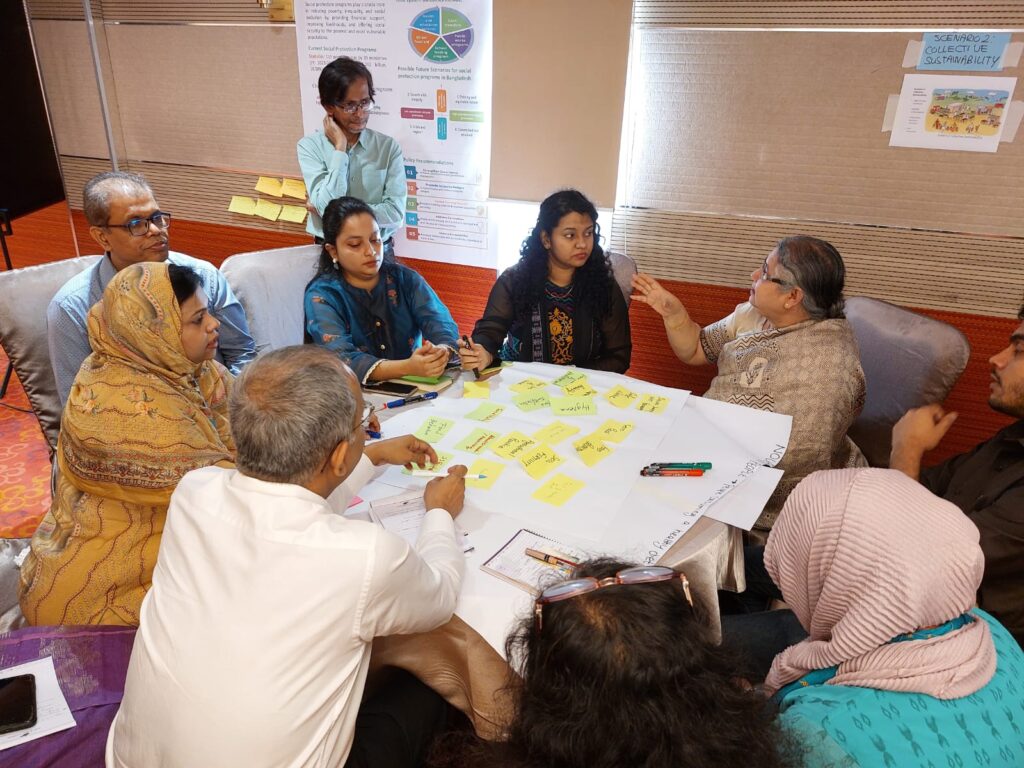



Reflections
Whilst having many people come together who don’t usually converse – the so-called ‘breaking the siloes’ is a huge achievement in itself, the task of writing yet another policy document looms above our heads. Everyone in the room has appeared here for a reason – which I hope is to create the change we need, a future that we all desire. After such positive discussions and recognition that we need to act – and act now, the fear I have is we will all fall into the same trap. The trap of being consumed by our busy agendas and becoming frustrated that yet another policy document has to be produced. Leading to un-actionable and hugely categorised actions. We don’t want this Plan of Action to become another document that has great suggestions but continues to lack the HOW. Let us think about how will these actions be implemented.
Foresight helps us to keep the bigger picture in mind, where do we want to go and where do we want to be in the future? Let’s use this thinking to help us prioritise and select key activities to implement. Working together to do so.
By Patrick Caron – President of Agropolis International, Montpellier, France
and Co-Chair Foresight4Food Initiative
In today’s rapidly changing world, it’s vital to reassess our approach to foresight if we aim to make meaningful transitions toward a better future. But first, I want to reverse the perspective. Why should we engage with foresight in the first place? Why should foresight be central to our strategy for navigating today’s uncertainties and transitioning toward a more sustainable world? This will enable us to see the value of foresight, while also urging us to explore new transitions in foresight practice itself.
Upcoming event
Join us for an insightful session on “Foresight Navigating Polycrises”, where we’ll explore how foresight approaches can evolve to help us navigate the complexities of today’s global polycrises.
The Polycrisis We Face
We are all aware that the world today is facing multiple, interconnected crises—what is increasingly referred to as a “polycrisis”. From climate change and environmental degradation to food insecurity, conflict, and mass migration, global interconnected crises are compounding in ways that make solutions more elusive. We see extreme weather events, challenges in livelihoods, and even migration crises, all feeding into one another. The agricultural and food sector provides a telling example of how this complexity plays out. In the 20th century, food security was often synonymous with simply increasing agricultural output to meet the needs of a growing population. But this approach no longer holds in the 21st century, where food systems must integrate issues like ecosystem health, social justice, and human well-being.
Beyond Agriculture: Foresight, Food Systems, and Global Goals
Foresight is essential for transforming food systems as it enables a long-term, integrated view of how food, health, climate, and equity intersect. As food systems now play a critical role in achieving multiple Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), foresight helps policymakers, researchers, and stakeholders anticipate future challenges like climate change, resource scarcity, and population growth. This forward-looking approach is key to navigating complex global challenges and achieving the holistic transformation called for by initiatives like the UN Food Systems Summit.
At the same time, the polycrisis demands a systems-level approach. The transformation of food systems is no longer about just ending hunger (SDG2), but about achieving multiple Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Food systems now lie at the intersection of climate action, health, equity, and sustainability. This complexity was highlighted at the UN Food Systems Summit in 2021, where the call for a holistic transformation of food systems became clear.






The Changing Role of Science
Science, too, is evolving. For much of the 20th century, there was a more linear view of science’s role: knowledge was generated, applied through technology, and action followed. Today, this model no longer applies. The polycrisis is too complex for linear solutions. We must embrace uncertainty, acknowledging that even science has limits and that collaboration across disciplines and sectors is essential.
Four Key Shifts for Foresight and Science
If we want to move forward, we need to embrace four critical shifts in how we think and act.
- From Forecast to Foresight
Forecasting has long been about identifying trends, but the future rarely follows a predictable path. We need to move beyond forecasts and embrace foresight. This means exploring multiple scenarios, understanding possible and plausible futures, and making decisions today that can shape those futures. Foresight, unlike forecasting, accepts uncertainty and the need for flexibility in planning.
- From Sectoral to Trans-Sectoral Action
Another key shift involves moving from siloed thinking to a trans-sectoral approach. Cities, nations, and scientific disciplines often focus on their own isolated priorities, which makes it difficult to address the interconnected nature of modern crises. For example, city officials may focus on water, transportation, or sanitation, while a Ministry of Agriculture focuses on food production, and scientists work within their own disciplinary boundaries. To address food security and other pressing global issues, we need to bring together health, agriculture, environment, and more into integrated solutions.
- From Certainty to Controversy
We also need to shift from seeking certainties to embracing and addressing controversies. Science has traditionally been about providing concrete answers, but in today’s world, differing perspectives and debates are inevitable. These debates are not just a sign of conflict; they are an opportunity to bring diverse views together to design better solutions. Rather than avoiding controversy, we need to engage in dialogue and even mediation, respect differing opinions, and work toward a shared understanding of why disagreements exist.
- Building Capacities for Collective Action
Finally, we must invest in developing capacities for collective action and innovation. It’s essential to create structures that allow diverse voices to be heard, including those who are often marginalized. We need to foster environments where science and policy can interact in meaningful ways, not through a simple transfer of knowledge, but through the co-creation of actionable solutions. This requires building institutional frameworks that support ongoing dialogue between policymakers, scientists, and communities.
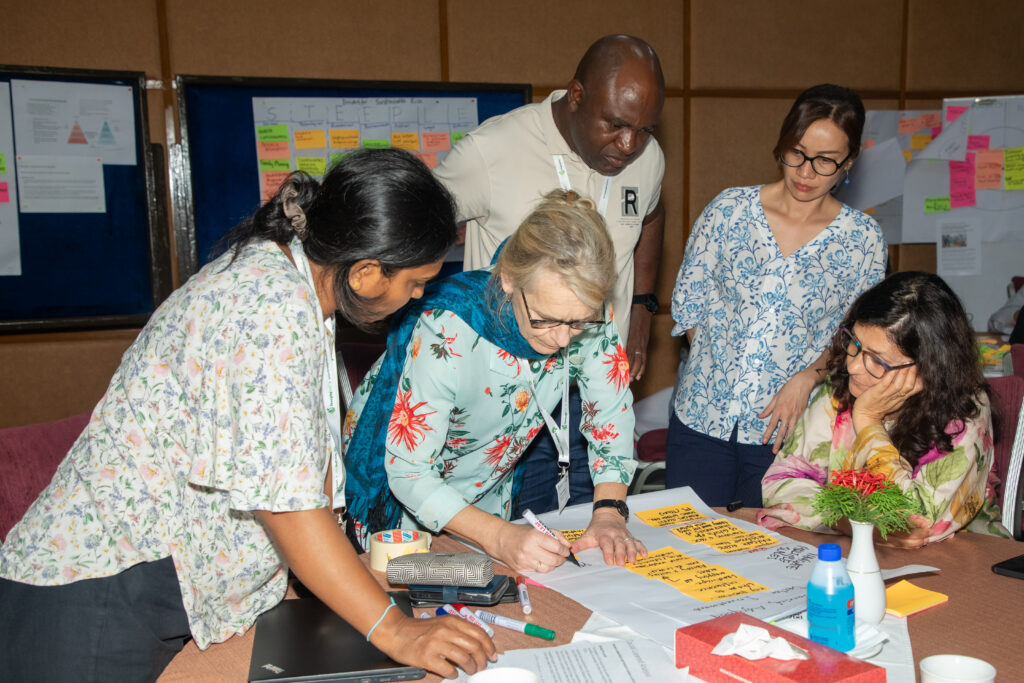



The Road Ahead – Foresight4Food and Global Change
Foresight4Food offers a way forward by pooling collective intelligence across agriculture, food, environment, and health. The path to a sustainable future lies in collaboration—across sectors, disciplines, and scales. From local to global, the interconnected nature of today’s challenges demands that we look beyond traditional boundaries. We must explore possible futures, engage with uncertainty, and develop innovative solutions that can help us move toward a more just and sustainable world.
The 2021 UN Food Systems Summit and other international initiatives, such as the Montpellier Process, show that while we are facing unprecedented challenges, we are also making strides in understanding how to address them. Foresight can help us navigate these complex dynamics, allowing us to envision a future where food systems, health, and environmental sustainability are addressed consistently.
In conclusion, our collective efforts should focus on fostering dialogue, embracing uncertainty, and developing capacities that will allow us to pool collective intelligence and shape the future. Only by breaking down silos and working together can we hope to navigate the polycrisis and create a better world for future generations.
The Foresight for Food System Transformation (FoSTr) programme, led by Foresight4Food, is now two years into its journey of helping shape more sustainable, inclusive, and resilient food systems. With increasing uncertainties affecting global food systems—from climate change to economic challenges—the need for foresight and scenario analysis has never been more critical.

Running from 2022 to 2025, the programme is funded by the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs through an IFAD grant. Based on the approach of the Foresight Framework, the programme focuses on supporting four key countries: Bangladesh, Jordan, Kenya, and Uganda.
Since its commencement, we have seen tremendous strides in advancing the key objectives of the FoSTr programme across multiple fronts. This blog highlights the progress and impact of the FoSTr programme and the exciting path ahead.
In-Country Impact: Strengthening Foresight Processes
In each of the focus countries, national foresight processes gained momentum, engaging a wide range of stakeholders, including government bodies, research institutions, and community representatives. In total, 403 individual stakeholders participated in in-country workshops across the four countries, contributing to meaningful conversations about the future of food systems.
Here is a quick overview of FoSTr programme’s progress in each of the focus countries:
Bangladesh – Strong government buy-in has been established, with collaboration from the Ministry of Food and other key players, all contributing to the national food system transformation agenda.
Jordan – Partnerships with the Ministry of Agriculture and other government entities have positioned FoSTr as a key advisor, particularly in driving forward the work of the newly established Food Security Council.
Kenya – Foresight analysis has been particularly active at both the national and county levels, with significant involvement from the Nakuru and Marsabit County governments.
Uganda – FoSTr is closely aligned with the Uganda Planning Authority, helping develop foresight tools for future food system planning.






Global Collaboration: Building a Brokering Hub
On a global scale, FoSTr expanded its network of foresight and food systems practitioners, deepening collaboration across organizations like the Forum for Agricultural Research in Africa (FARA), the Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition (GAIN) in Bangladesh, and a number of renowned research institutes in the focus countries.
The work of FoSTr programme was very well-received at the 4th Global Foresight4Food Workshop in Dhaka, where more than 120 foresight practitioners from Asia, Africa, and Europe gathered to share insights on foresight methodologies and food system challenges.
Read also:
Using Foresight to Re-imagine the Future of Food Systems: Foresight4Food holds its 4th Global Meeting – by Jim Woodhill
In a highly interactive week, participants engaged in a masterclass on foresight approaches, shared their experiences and lessons, heard from thought-leaders on food systems and foresight, and identified ways of strengthening foresight practice in their own countries and regions…
A Start to the Foresight Process: Food Systems Maps
As a part of the foresight process, there is a need to have a collective understanding of the food system in different contexts. Hence, the Foresight4Food FoSTr team in collaboration with our facilitators and research partners in each focus country, created comprehensive food systems reports mapping the dynamics, trends, drivers, and activities within the food system.
These Food System Maps offer an initial snapshot of the current food system status in the focus countries and are intended to inform a more comprehensive foresight process. As the dynamics, trends, drivers, and activities within the food system continually change, these reports welcome ongoing reflection and discussion.
Knowledge Base
FoSTr also played a vital part in strengthening the Foresight4Food Resource Portal, which provides access to Foresight Studies, key data around Food System Drivers and Outcomes, a database of Foresight Initiatives, and other academic literature that helps food systems practitioners develop better Foresight Models.
The Foresight4Food Resource Portal is regularly updated with the latest research and emerging studies as well as products and resources that come out of different programme activities.
Read also:
The Complexity of Global Drivers of Food System Transformation – by Bhawana Gupta
The global food system needs to be transformed. It needs to deliver better health and improved livelihoods while protecting the environment and minimizing negative social impacts. However, there are many interconnected factors playing a role. Food Systems are complex…
Overcoming Challenges
Like any ambitious programme, FoSTr encountered its share of challenges. These included navigating political instability in some focus countries. Meanwhile, navigating the political economy of food systems—especially where entrenched power dynamics and vested interests are at play—required FoSTr to strike a delicate balance between supporting ongoing policy processes and introducing more transformative ideas for change.
The Way Forward
As the Foresight4Food FoSTr programme enters its third and final year, several key objectives will guide the remaining activities:
Brokering Foresight Processes: Continue to build connections with national stakeholders and existing initiatives, ensuring that foresight insights are integrated into policy-making and planning processes.
Capacity Building: Organize intensive face-to-face training workshops to further enhance foresight facilitation skills and broaden participation from underrepresented groups, including the private sector and youth.
Scenario Analysis and Policy Recommendations: Complete the ongoing scenario analyses and translate these into clear policy recommendations that will guide national food system transformation agendas.
Sustaining Momentum Beyond 2025: Establish sustainable communities of practice that can continue to drive foresight activities beyond the programme’s official end.
Conclusion: A Transformative Journey
In an era where global food systems are under immense pressure due to climate change, population growth, and shifting socio-economic landscapes, forward-thinking approaches are critical to ensuring food security and sustainability.
The Foresight4Food FoSTr programme has made significant headway in its mission to advance food system foresight processes in Bangladesh, Jordan, Kenya, and Uganda while building a broader global network of foresight practitioners. As we look ahead to the final year, the focus will be on translating foresight insights into action, empowering national stakeholders, and ensuring that the work of FoSTr continues to have a lasting impact on food systems worldwide.
Bonus: FoSTr Facilitators Insights
As the Foresight4Food FoSTr programme continues to foster systemic change in global food systems, the programme facilitators will be sharing their observations on the work and progress of FoSTr programme in their respective countries through insightful blogs. Watch this space and our social media channels for more updates.
By Bhawana Gupta, Monika Zurek, and John Ingram
In a world facing unprecedented uncertainties, the futureproofing of policies has become more crucial than ever. Foresight tools and methods, widely used across various sectors, play a pivotal role in supporting decision-making by providing an evidence base for assessing challenges, prioritising issues, sense-making, preparing a targeted action plan, and conducting risk assessments.
However, the challenge often lies in aligning these foresight activities with the policymaking cycle to create coherent, impactful policies. This blog provides a glimpse of an ongoing Foresight4Food study in Bangladesh, Jordan, Kenya and Uganda under the Foresight4Food FoSTr programme that explores how foresight tools can be systematically integrated into the policymaking cycle to enhance their utility and contribute to better policy outcomes.
The gap in current practices
Despite the widespread use of foresight methods, there is often a lack of clarity on how their outcomes can feed into decision-making. The foresight activity is frequently not recontextualized for the specific policy problem at hand. This disconnect poses a significant challenge, as the integration of foresight into the policymaking cycle is crucial for developing more resilient and future-proof policies. The goal is to bridge this gap by providing evidence on the most useful foresight tools and methods for each part of the policymaking cycle.
When foresight is integrated into the policymaking cycle, it ensures that future-oriented thinking is consistently applied throughout the policy development process, leading to more coherent and effective policies.
Read also:
The Complexity of Global Drivers of Food System Transformation – by Bhawana Gupta
The global food system needs to be transformed. It needs to deliver better health and improved livelihoods while protecting the environment and minimizing negative social impacts. However, there are many interconnected factors playing a role. Food Systems are complex…
Importance of linking foresight with the policy cycle
Integrating foresight processes with the policy cycle is essential to institutionalize foresight and enhance its usability at national and local levels. Institutionalizing foresight ensures that these methods are systematically applied, enabling policymakers to anticipate and prepare for future challenges effectively. It also ensures inclusiveness and rigour of the policy-making process.
Such work can draw on the experience in several high-income countries have successfully institutionalised foresight within their policymaking structures, demonstrating the benefits of this approach. Some examples are:
- Finland: Finland has a well-established foresight system integrated into its national policy framework. The Finnish Government Foresight Group coordinates foresight activities across various sectors, ensuring that long-term trends and future scenarios are considered in policymaking.
- Singapore: The Centre for Strategic Futures (CSF) in Singapore plays a key role in incorporating foresight into government planning. CSF conducts scenario planning and horizon scanning to support strategic decision-making and policy development.
- United Kingdom: The UK Government Office for Science runs the Foresight Programme, which explores future challenges and opportunities. This programme provides evidence-based insights to inform policy decisions across different government departments.
But what led to the establishment of foresight institutions as an integral part of the policy-making bodies in these countries? It’s the awareness, capacity building and the demand for foresight knowledge which have been crucial. Foresight4Food is playing a major role in its case study middle- and low-income countries in instigating the adoption of foresight across all levels of decision-making processes.
How our research is guiding foresight in middle and low-income countries
While high-income countries have made significant strides in institutionalising foresight, it is equally important for middle- and low-income countries to adopt these practices. The challenges faced by these countries, such as rapid urbanization, climate change, and economic volatility require proactive and informed policy responses.
Research on the appropriate foresight methods for different policymaking stages can significantly aid in institutionalising foresight in such countries by ensuring targeted application and resource efficiency, thus maximising the value of foresight activities. By pinpointing specific methods for each policy stage, governments can allocate limited resources more effectively, avoiding a one-size-fits-all approach. This tailored research provides a clear framework for capacity building, enabling policymakers to apply foresight methods appropriately across different policy stages. Demonstrating the practical benefits of specific methods enhances decision-making, supports institutional integration, and fosters a culture of foresight within government institutions.

Furthermore, it ensures policy coherence and continuity, establishing standardized foresight practices that maintain consistency even amidst political and administrative changes, ultimately promoting the institutionalisation of foresight in these countries.
Understanding the policymaking cycle
Institutional decision-making follows a structured sequential process known as the policymaking cycle, which guides actions and outcomes through distinct stages. Governments worldwide have adapted this cycle to develop new policies or reform existing ones. This model provides a clear and organized way to understand and analyse how policies are developed and executed.
However, in reality, the policymaking process is rarely this straightforward. It is typically non-linear, iterative, and influenced by a multitude of factors including political dynamics, stakeholder interests, and unexpected events. Despite this complexity, the policy cycle remains an important framework for several reasons but most importantly the principles underlying the policy cycle—such as systematic analysis, stakeholder engagement, and evidence-based decision-making—remain relevant. These principles provide a foundation for effective policymaking, guiding policymakers in navigating the complexities and uncertainties of the real world.
Understanding the policy-cycle stages is the first step, as it allows foresight practitioners to identify where future-oriented insights can be most impactful, ensuring that long-term considerations and potential future scenarios are effectively embedded into the policymaking process. This structured approach enhances the relevance and applicability of foresight outcomes, leading to more robust and resilient policies.
There are many examples of these policy cycles that have been developed and adapted but the essence remains consistent. Typically, it includes stages such as issue identification, policy identification, policy adoption and implementation, and lastly policy monitoring and evaluation. This cycle serves as a valuable model to explore which foresight tools/methods can generate insights needed for processing in the policy cycle.
Mapping foresight methods to policymaking stages
Foresight4Food researchers mapped more than 50 foresight tools and methods that have been implemented for a range of purposes. Sometimes the same tool was used for different purposes, which changes the way the tool was used and applied. Foresight methods can therefore serve various purposes at different stages of the policymaking process.
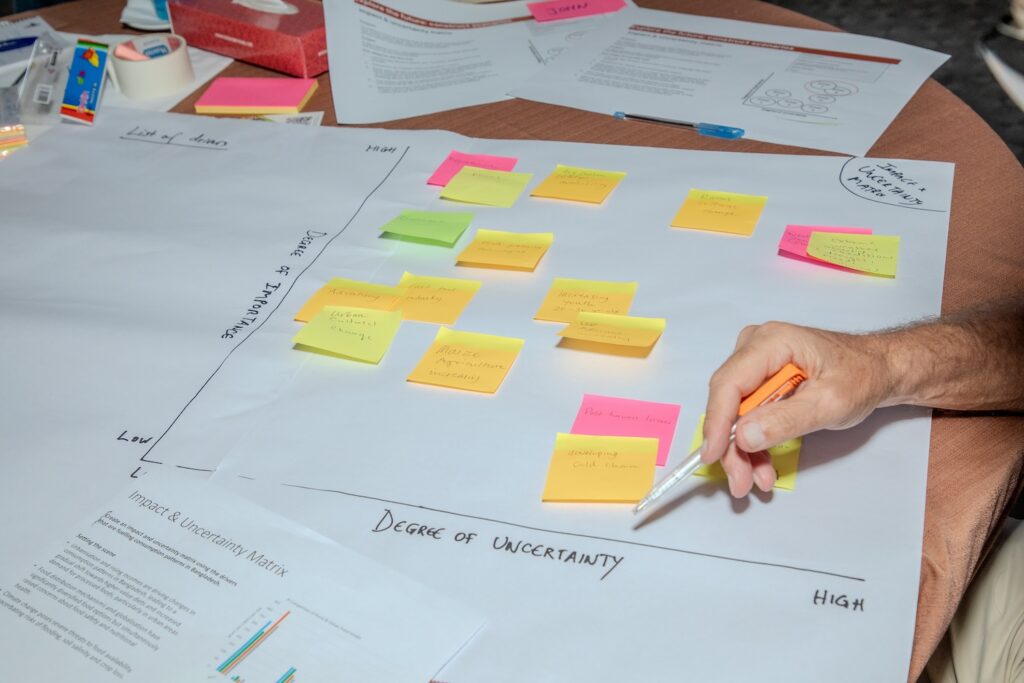


This study highlights several models of the policymaking cycle and how foresight tools can be mapped onto these stages. For example:
- Agenda Setting: Foresight can generate information on challenges, drivers of change, and options for tackling problems, which directs policymakers to develop a policy concept and contextualize the emerging problem.
- Policy Formulation: Scenario planning and trend analysis can help in developing policy options and assessing their potential impacts.
- Policy adoption and implementation: Participatory approaches and Delphi methods can facilitate inclusive participation and build consensus on the preferred policy option. Horizon scanning and risk assessments can enhance policy implementation by raising awareness of future changes and building networks for understanding visions among stakeholders.
- Monitoring and evaluation: Backcasting and impact assessments can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of implemented policies and provide a basis for future decision-making.
In conclusion, integrating foresight tools into the policymaking cycle is crucial for developing more resilient, future-proof policies. While high-income countries have demonstrated the value of institutionalizing foresight, it is vital for middle- and low-income countries to also adopt these practices to address their unique challenges and opportunities. By systematically linking foresight with the policy cycle, policymakers can create more informed, adaptable, and sustainable policies, ultimately contributing to better outcomes for society.
By Bram Peters
The Foresight4Food FoSTr team has just returned from an active and productive trip to Kenya, despite the challenging political situation in the country. From our perspective, this highlights the need to adapt to turbulence and to use foresight to build resilience for Kenya’s food system.
From June 19 to 26, together with my team members including Jim Woodhill, Herman Brouwer, and Wangeci Gitata-Kiriga we conducted a range of food systems foresight workshops in Nairobi and Nakuru with a wide range of national food systems stakeholders. Here is a brief update on the action.
Navigating turbulence
On the morning of June 19, Foresight4Food, together with partners ILRI–CGIAR, Results for Africa Initiative and University of Nairobi, organised two sessions in Nairobi. The interactive breakfast session was all about ‘Navigating agri-business in turbulent futures’. The session was co-hosted by IFAD Kenya and was attended by a range of private sector associations, business support services, innovation facilitators and impact investors.

The focus of the meeting was to introduce the topic of foresight in relation to agribusiness in Kenya, share some of the scenarios that were developed in the context of Nakuru, and discuss the implications of different futures of the food system. Participants were shown five different scenarios of how the food system might look in 2040 in Nakuru and were invited to think through and discuss the implications of these scenarios.



With a strong presence and involvement of leaders from various private sector associations such as the Agriculture Sector Network (ASNET) of the Kenya Private Sector Alliance, the discussion invited stakeholders to reflect not only on trends and uncertainties emerging in Kenya, but also how their own businesses are preparing for the future.
Supporting the pathways for food system transformation
In the afternoon of June 19, the FoSTr team organised a national update session on the progress of FoSTr since June 2023. The session was attended by many individuals from the morning session, as well as representatives from government, civil society and research organisations. The FoSTr team presented the latest updates, including the launch of a ‘Kenya Food Systems Mapping Report’, and with a collection of scenarios for the Nakuru food system.

With a special presentation by the Ministry of Agriculture and the Food Systems Technical Working Group and special remarks from IFAD on the 3FS tool, it was discussed how a wide range of ecosystem support initiatives are buttressing the national food systems transformation pathways in Kenya. The approach by Foresight4Food to engage with two counties, Nakuru and Marsabit, and to build on Bottom-up initiatives showed how our approach complements the ongoing national-level initiatives.
Systemic Theory of Change
From June 19 to 21, the Foresight4Food FoSTr team facilitated a 3-day workshop for the inception phase of the new Netherlands-funded, World Food Programme and UNESCO on ‘Sustainably Unlocking the Potential of Lake Turkana. Stakeholder representatives from the Lake Turkana region (both on the Marsabit and Turkana sides of the lake) gathered in Nairobi to engage in a shared analysis of the complex food system and co-create the high-level focus of the programme.
The Turkana Lake food system is highly complex, with high food insecurity, vulnerability to climate change and conflict, and many cultural dynamics around pastoralist and fisheries livelihoods. Finding market opportunities and strengthening resilience is not easy, and requires a different way of working. Using the Foresight4Food approach, and building on 6 scenarios that were developed in previous workshops in Marsabit and Turkana, stakeholders explored what might need to be done to understand systemic risks and how lasting opportunities can be triggered.
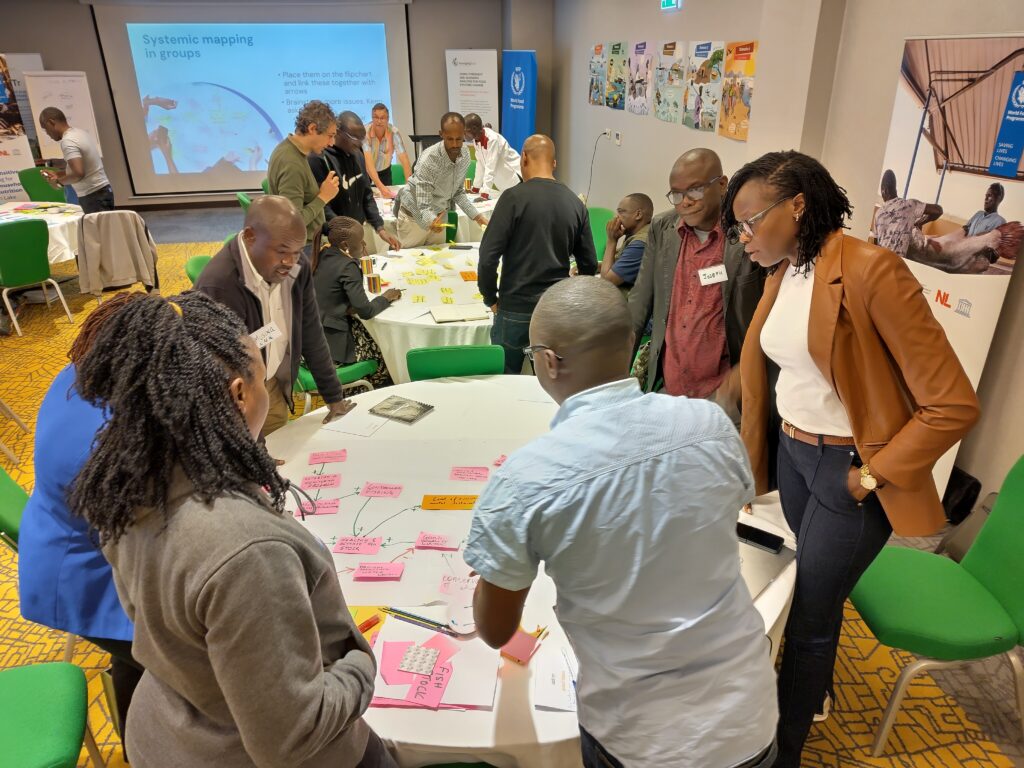



Preparing a Systemic ToC is all about analysing the context, articulating the transformations needed in light of various future scenarios, and developing the building blocks for action. The building blocks include pathways, processes and partnerships. Through many interactive discussions and exercises, the stakeholders conducted value chain mapping of the fish value chain, CATWOVE for articulating systemic change narratives, and Causal Loop Mapping.
Manifesto for Change for the Nakuru Food System
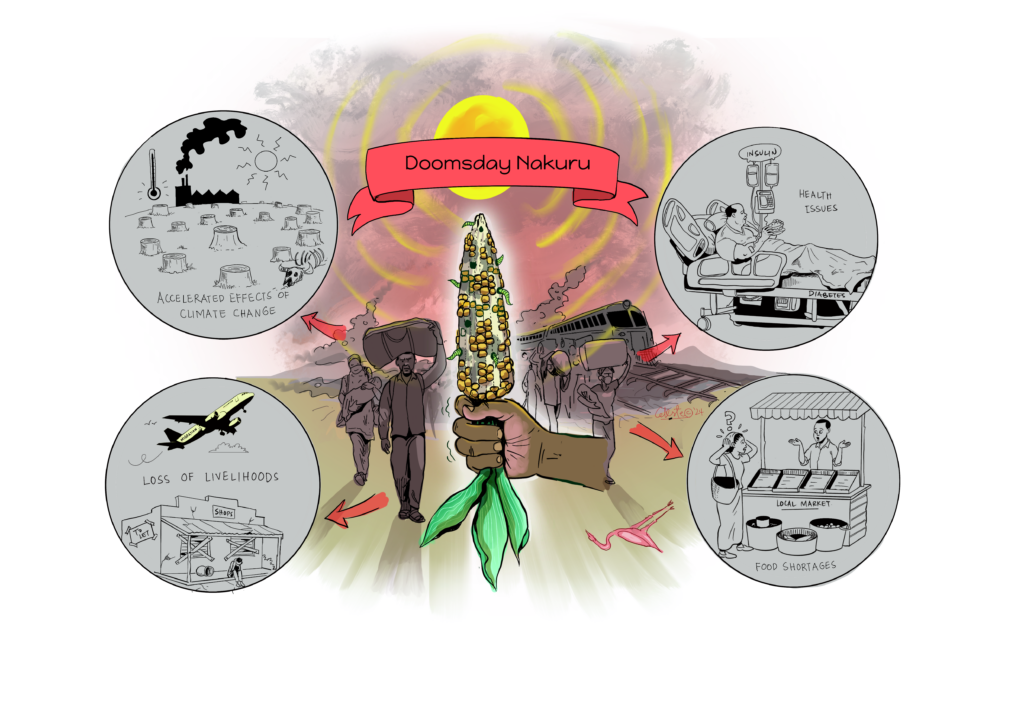
On June 24 and 25, the FoSTr team including partners ILRI-CGIAR, Results for Africa Initiative and University of Nairobi once again visited Nakuru, now to explore systemic change pathways. As we already noted from previous workshops, the food system of Nakuru County is full of potential, as Nakuru’s natural resources are rich and a wide range of agricultural value chains are represented. However, challenges related to food and nutrition security and environmental sustainability exist. Trends of climate change, unhealthy diets and land fragmentation are appearing. The future holds many uncertainties. In order to future-proof the food system, it is urgent that investments are made to further enhance the resilience and sustainability of food and agriculture in Nakuru.
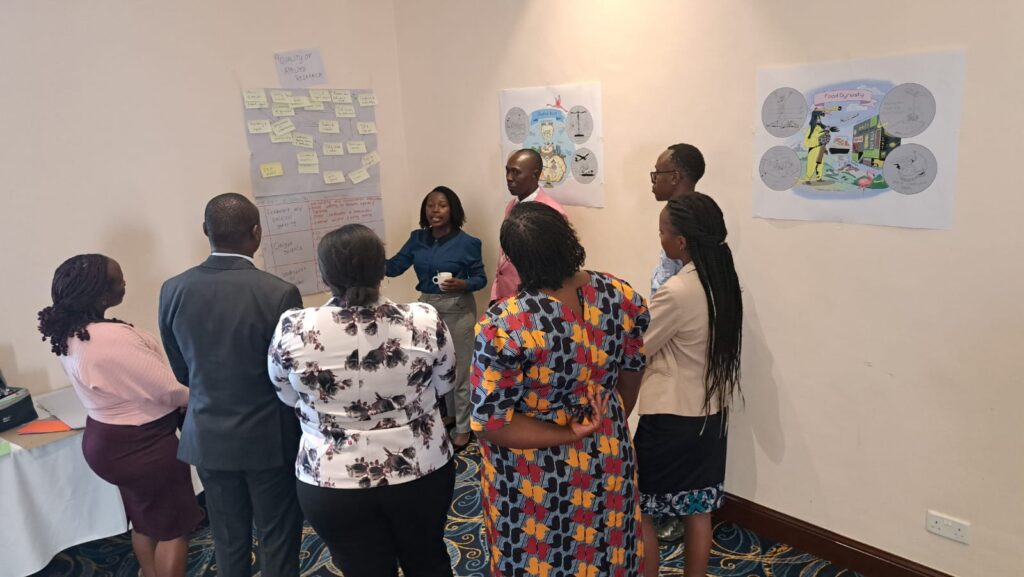



Since November 2023, a diverse group of more than 40 different stakeholders from Nakuru county have been coming together to consider the future of food system, supported by researchers and facilitators of Foresight4Food. This inclusive group looked at the challenges and opportunities for food and agriculture today and how they might evolve in 10-15 years. Food system analysis, an assessment of drivers and trends relevant to Nakuru, and 5 scenarios were developed by this group.
During these two days, stakeholders from Nakuru engaged in scenario interpretation and Causal Loop diagramming to come up with key pathways to kickstart food system transformation in Nakuru. These outputs culminated in a Manifesto for Change: a vision for the desired future for Nakuru’s food system and a range of possible pathways that can set us in that direction, while preparing us for a range of uncertainties. The Manifesto calls upon all stakeholders to join and align their actions, and intensify collaboration to transform Nakuru’s food system so that it can feed its people nutritiously; advance economic development; restore balance with nature; grow in-county revenue and eventually GDP growth for Kenya.
By Zoe Barois
Over the past year, the Foresight4Food Foresight for Food System Transformation – FoSTr team and our country partners have begun a foresight process in Jordan, Uganda, Kenya, Bangladesh, and Niger to support national food system transformation. As an initial step, a collective understanding of the food system in different contexts was needed. Hence, the Foresight4Food team in collaboration with our facilitators and research partners in each focus country, created comprehensive food systems reports mapping the dynamics, trends, drivers, and activities within the food system.
Being a lead on food system mapping, I’m sharing my reflections on the process in this blog.
We started with a scoping phase using the Foresight4Food foresight framework, which allows for flexibility and contextual adaptation. This phase involved identifying key stakeholders, understanding their interests, and assessing current and future concerns.
Our next goal was to foster a shared understanding of the food system’s key dynamics, outcomes, drivers, and activities to identify trends and uncertainties. This collective understanding forms the foundation for a participatory process using foresight and scenario analyses to support meaningful food systems change.
The second step, system mapping, was done in collaboration with country facilitators and research teams. We used the Foresight4food framework to identify key food system outcomes, activities, and drivers, considering their interaction with the broader environment. Data were compiled from national and global sources and generated through participatory workshops.
In addition to providing an overview of current status and trends, we conducted a deeper analysis using causal loop diagrams created with research partners during workshops. This approach helped identify trade-offs and synergies, informing actions to improve food system outcomes. We also noted recurring patterns that affect feedback loops, further clarifying the system’s structure.
These reports offer an initial snapshot of the current food system status and are intended to inform a more comprehensive foresight process. As the dynamics, trends, drivers, and activities within the food system continually change, these reports welcome ongoing reflection and discussion.





Read and download reports
The global food system needs to be transformed. It needs to deliver better health and improved livelihoods while protecting the environment and minimizing negative social impacts.
However, there are many interconnected factors playing a role. Food Systems are complex adaptive systems which require a deep analysis of their various driving forces and dynamics. They are shaped by a multitude of interconnected factors or drivers, some well-defined, others with a lot of uncertainties with them. A recent study by Forsight4Food identified the most critical drivers of the global food system as described by a set of 19 recent foresight reports. It was not easy to define and categorize these very drivers, and we will also discuss these challenges in this blog.
The Entangled Web of Drivers
Many studies, from the 2003 Millennium Assessment report to FAO 2022 have defined what is a ‘driver’. But the challenge is the lack of a universally agreed-upon definition for a driver. This means that categorizing these drivers is problematic. For instance, they can be classified based on their relationship with other drivers (direct or indirect), external factors (like PESTLE analysis- Political, Economic, Sociological, Technological, Legal and Environmental), or the extent of our knowledge about them (known knowns or unknown unknown).
What makes it even more intricate is that, due to the systemic nature of the food system, its nutrition, environmental condition, and economic development outcomes feedback indirectly becomes driver themselves. This creates feedback loops that complicate pinpointing which drivers are truly direct and which are indirect. Ultimately, it depends on the specific part of the system you’re focusing on. This is nicely depicted in the FAO’s food system diagram, however, it does not show the interconnections between different factors which is what needs careful consideration.
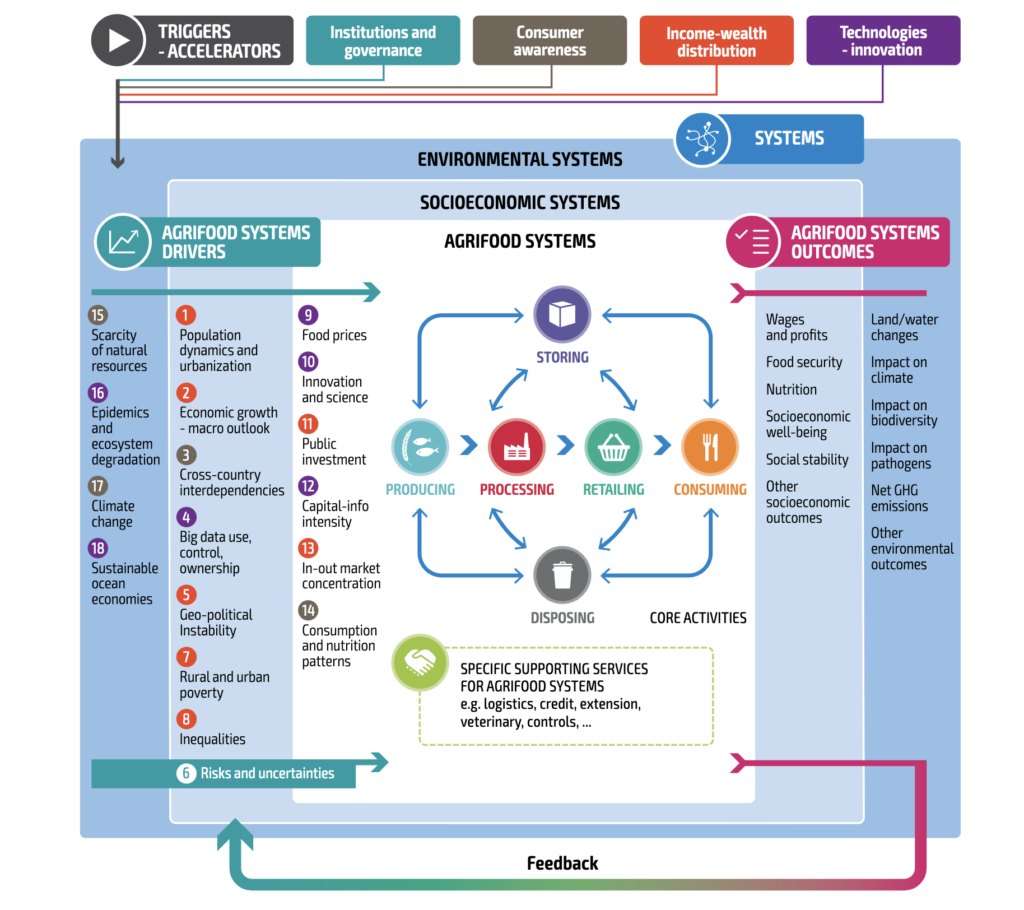
Source: FAO 2022
Here’s another layer of complexity: There are “known knowns” drivers like climate change and population growth and many models have been developed to understand the future trend. Then there are drivers such as government interventions (trade policies and subsidies) which is undoubtedly an important driver, but predicting the future impact of specific interventions is challenging. Similarly, we understand that diets are shifting towards more protein, but whether this trend holds true depends on the specific scenario we’re considering. These are “known unknowns” – we know they exist, but their future impact is a mystery. But the complexity is even deeper: “unknown unknowns”. Take the influence of social media on food choices. This is a relatively new area of study, and its full impact on the food system remains unclear. There can be overlaps in any type of categorisation system. Therefore, it is important to involve experts at this stage.
Identifying the Critical Few
The next hurdle is identifying “critical drivers” – those with the most significant potential to impact the food system. These drivers can influence various stages through established historical trends or emerging uncertainties. A key challenge lies in determining their relative importance across diverse contexts, often depending on stakeholder perspectives. For instance, immigration policies can have a significant impact on agricultural workforces in some regions. Incorporating stakeholder consultations is crucial to prioritize the most impactful drivers in these specific contexts.
Keeping the Conversation Open
It’s vital to remember that the impacts of drivers manifest differently across various socio-economic settings and among different food systems stakeholders. Highlighting the context in which a driver is critical helps us develop more targeted solutions.
We must also acknowledge that new or emerging drivers with unclear trends can also have profound impacts. For example, as mentioned earlier, the role of social media in influencing food choices is a relatively new area of study.
Therefore, the conversation around identifying critical drivers needs to be open to periodic updates. As we uncover new information and witness the emergence of new drivers, we can refine our understanding of the food system and adapt our strategies accordingly.
Future Trends and Projections
The future trajectory of these drivers is influenced by various factors, both internal and external to the system. Climate change, consumer behaviour, and technological advancements all play a role in shaping the path ahead. These complexities of cross-impacts create uncertainties about the future, often interpreted through different assumptions in various projections.
Many reports from IPCC, FAO and UNDP present some of the trends and projected trends around food system drivers. But these vary due to the underlying assumptions. Moreover, deciphering these projections can be challenging due to two key factors: 1) varying timescales and 2) diverse representations of what a sustainable food system actually looks like. However, by delving deeper into these assumptions and comparing them, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the possible futures that lie ahead.



What we found…
The review of recent studies on food system drivers revealed a mix of established and emerging influences. We categorised drivers using the known-knowns and known-unknowns classification. Long-standing factors like demographic changes, climate issues, technological innovation, resource efficiency, socio-economic inequalities, government interventions, health considerations and level of connectivity continue to shape food systems, while new drivers such as the rise of e-commerce post-COVID-19, concerns about power imbalances in food value chains, labelling and packaging, data ownership issues, the role of indigenous knowledge, labour migration policies and perceptions around vegan and vegetarian diets are gaining importance. The relevance of these drivers varies based on stakeholder perceptions, indicating the diverse issues decision-makers must consider for effective management and adaptation.
The review also noted varying levels of uncertainty associated with these drivers. Established drivers, such as demographic trends, have narrower uncertainty ranges due to extensive research, leading to more consistent projections. However, differences in time frames, methods, and assumptions among studies complicate direct comparisons of quantitative trends. Emerging drivers, like government interventions and social media’s influence on consumer behaviour, exhibit broader uncertainty ranges and diverse trend directions, making them particularly significant for developing future scenarios. Our upcoming report will discuss these critical points in detail.
Conclusion
Transforming global food systems to deliver better outcomes is a complex and urgent challenge. Understanding the critical drivers shaping these systems, both well-known and emerging, is essential for creating the societal understanding and political will needed for meaningful change. Just as a map evolves with new discoveries, our understanding of these critical drivers needs constant refinement. Through ongoing research, collaboration, and open communication, we can navigate the complexities of the food system and support targeted solutions towards a more sustainable food system.
The preparations for the 4th Global Foresight4Food Workshop are well underway. A diverse group of participants are expected to join and use this opportunity to share their ideas and insights as well as connect with a growing community of foresight practitioners. In regard to this, we asked Dr. Rathana Peou Norbert-Munns, Sustainable Development, Agrifood System Policies and Climate Foresight Planning Specialist at FAO and a valuable member of the Foresight4Food steering group to share some thoughts and her expectations from the workshop.

The biggest challenge our world is facing that keeps me up at night…
If I had to pinpoint the most significant challenge, it would undoubtedly be climate change. However, as a foresight planning specialist, I’d say that a forward-thinking planning approach helps various stakeholders recognize not only the widely acknowledged issues but also those that are just beginning to emerge, the so-called early signals. These insights enable us to map out risks across multiple time horizons and envision plausible futures and encourage us to rethink our current actions and adopt innovative approaches which are urgently need it. Ultimately, while these concerns sometime disrupt my sleep, it definitely fuels my daily actions with a clear, long-term vision for sustainable change.
What I look forward to in the 4th Global Foresight4Food workshop
My expectations are set high to leverage the tool of Foresight for Food System Transformation effectively. In a global polycrisis, there is a pressing need for innovative and strategic thinking to guide decisions that ensure sustainable food systems.
This year’s theme of the Foresight4Food Global Workshop captures the essence of what we aim to achieve: a shift in how we envision and shape the future of food systems. It promises to be a crucial platform for sharing insights, fostering collaborative efforts, and enhancing the capabilities of practitioners through knowledge exchange and community building. It is an opportunity to connect with a diverse network of experts and stakeholders, all driven by the common goal of transforming food systems for a better future. By creating a safe space for discussion and reflection, the workshop will challenge us to consider innovative accelerators for our work and identify necessary changes in our approaches.
“This year’s theme of the Foresight4Food Global Workshop captures the essence of what we aim to achieve: a shift in how we envision and shape the future of food systems.”
The workshop will also allow us to critically assess vested interests within the food systems, ensuring that our solutions are inclusive and equitable, truly embodying the principle of leaving no one behind.
On a personal level, I expect that the insights I’ll gain from the workshop will be integral to refining approaches developed for key programs in the Asia Pacific region. By learning the latest foresight methodologies and emerging trends, I aim to reflect with an increasing community of practitioners and find avenue to collaborate more effectively with stakeholders to implement resilient and sustainable food policies and practices.
Some ways to make the workshop more effective, my two cents
To ensure the workshop has a lasting impact on cross-sector collaborations and actions towards food system transformation, Foresight4Food must foster an environment of honesty where participants feel secure in openly sharing both challenges and innovative ideas. Encouraging creative and bold thinking is essential, as it will drive the development of groundbreaking strategies that transcend traditional sector boundaries and catalyze meaningful changes through transformative foresight.